This project has been created as part the 42 curriculum by vpogorel.
The goal of this project was to familiarize ourselves with IP addressing within the TCP/IP model. We had to configure the IP adresses and network interfaces of 10 simulated networks with routers, switches and connected computers.
It's a framework of protocols that ensures the transmission of data across networks (including the internet). The communication protocols are organized in 4 layers of different purpose: Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Access.
Application Layer
Consists of different protocols that are necessary to communicate between applications across a network:
- Web: Browser ↔ Webserver (
HTTP,HTTPS) - Email: Mail client ↔ Mail server (
SMTP,IMAP,POP3) - File transfer: Client ↔ Server (
FTP,SFTP) - Remote connection: Admin ↔ Server (
SSH)
Transport layer:
The transport layer is responsible for the transmission of data between two services on different devices. It provides protocols that ensures delivery of data packets between these applications.
Most common transport layer protocols are TCP or UDP.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocoll) garantees a connection by ensuring data delivery through error detection, retransmission of lost packets and correct ordering of data (contenction oriented data delivery).
On the other side UPD (User Datagram protocol) is faster and connectionless protocol that doesn't garantee the delivery. It is commenly used in applications where speed is more important than reliability (Streaming (video/audio), online gaming or VoIP (Voice over IP)),
Internet layer:
The Internet layer is responsible for the identification of computers within a network and the selection of the most efficient paths or routes between networks. The Internet Protocol (IP) provides for each device a unique 32 bit number (ip address). Based of the destination IP the protocol picks the most efficient paths to reach the destination host. The core functionality of this layer are logical addressing (IP addressing), rounting (selecting the best path) and packet forwarding to the destination network.
Network access layer:
The Network Access Layer is responsible for moving data between devices on the same physical network (Wi-fi, ethernet, ...).
You watching a video on a website.
Application layer: HTTPS
Transport layer: UDP
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is set of rules that governs how computers communicate reliably over a network. Therefore it breaks data into small packets, sends them over the network and ensures they are delivered error free and in the correct order at the recipient.
The Internet protocoll (IP) is a protocoll and used for routing and addressing across networks. In IPv4 an address is a 32-bit long number and is divided into 4 octets (8-bit-segments).
"number1.number2.number3.number4" or "XXXXXXXX.XXXXXXXX.XXXXXXXXX.XXXXXXXXX"
198.98.23.23 or 11000110.1100010.00010111.00010111
An IP address has a network and a host part.
all number in the range 0-255.
For example:
| Class | IP Range |
|---|---|
| class A | 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 |
| class B | 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 |
| class C | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
local ip for internal use: 127.0.0.1 - 127.255.255.254
Broadcast address is the address that sends to every host of a network a message.
The network address is an unique identifier which will be assigned to each device in a network.
The subnetmask is a 32 bit long number and useful to calculate the network or host address of ip address.
Subnetting describes the division of network into smaller subnetworks. Depeding of bits in the netmask you can devide the network into smaller networks.
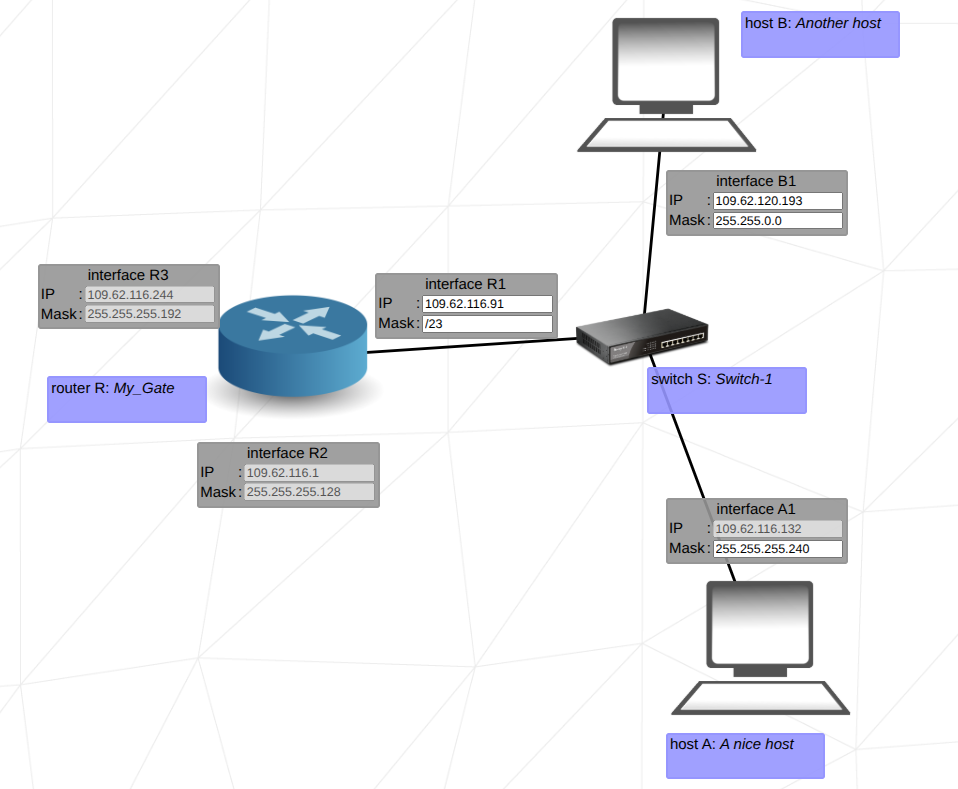
A router is a network device that connects networks and routs data between them. It makes forwarding decision based on the ip address and routing tables. A Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns a public ip to the router in order to connect the local network (lan) to the internet.
A default gateway is the router that a device uses to send traffic to another network. When a host wants to communicate with an IP address outside its local network, it forwards the packet to the default gateway, which then consults its routing table to determine the next hop.
A switch is network device that connects mutiple devices in lan and forwards data only to devices with a corresponding MAC address.
To run and use this project:
- Open the training interface:
Openindex.htmlin a web browser. - Interact with the network simulation:
Configure devices, establish connections, and complete exercises as specified in each level. - Export configurations:
After completing a level, export your configuration. This generates a file containing your network setup. - Submission:
Place all 10 exported configuration files (one per level) in the root of your repository.
-
Networking References:
- TCP/IP Basics: https://www.ietf.org, [https://edu.anarcho-copy.org/TCP%20IP%20-%20Network/TCP-IP%20For%20Dummies.pdf]
- OSI Model Overview: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/what-is-the-osi-model.html
- Routers and Switches: https://networklessons.com
-
AI Usage:
AI was used to assist in [e.g., generating configuration templates, providing hints for exercises, verifying network setups]. Specific tasks include:- Suggesting subnet allocations based on user input
- Validating connectivity between devices
- Generating sample configuration files for each level
- genarating descriptions of network terms
-
Tutorials and Articles:
- Networking Fundamentals Tutorial
- Subnetting Guide
- [IP calculator] (https://jodies.de/ipcalc)